This blog post is an excerpt from my latest open-access article on the intersection of open innovation and the circular economy.
Suggested citation: Camilleri, M.A. (2025). Cocreating Value Through Open Circular Innovation Strategies: A Results-Driven Work Plan and Future Research Avenues, Business Strategy and the Environment, https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.4216

The stakeholders’ open innovation approaches are evidenced through collaborative practices across value chains, as practitioners are willing to share ideas and technologies with “new” partners to advance disruptive sustainable innovations (Battistella and Pessot 2024; Bocken and Ritala 2022; Brown et al. 2020). Inbound innovation practitioners can benefit from external stakeholders’ knowledge and expertise to implement product-life extension strategies and resource recovery methods and to cocreate circular economy ecosystems including industrial symbiosis, reverse logistics, product-service systems/product-as-a-service, sharing economy, and leasing models (Köhler et al. 2022; Lisi et al. 2024).
Resource Recovery and Industrial Symbiosis
Open innovation practitioners would benefit from external competences, capabilities, and technologies from stakeholders who are not in the company’s books. Their ongoing engagement and collaboration with them may help them improve their operations as they acquire resources such as human capital, materials, energy, water, and by-products, among others. Resource sharing can help the businesses to optimize manufacturing processes, to minimize waste, and to create a more sustainable and efficient industrial ecosystem (Johnstone 2024).
Practitioners may even benefit from other businesses’ externalities including by-products or unwanted waste materials and could utilize them as resources. They can leverage open innovation approaches to address resource scarcity (and resource depletion) by finding new ways to repurpose waste. They may do so by reducing material inputs and by recycling valuable resources (Berkemeier et al. 2024). For example, the heat generated from a power plant could be used to heat buildings or greenhouses located in nearby communities. Industries situated close to each other may share utilities including energy and water supply infrastructure or services, such as transportation, water treatment facilities, or waste management services. Their resource recovery can result in cost saving and operational efficiencies (Johnstone 2024).
Cross-industry collaboration and industrial symbiosis can help companies to discover new uses of waste streams to develop circular supply chains. There is scope for business leaders to engage with external stakeholders, to exchange or sell discarded resources, and by-products that would otherwise end up as waste. Arguably, one company’s waste, materials and by-products can serve as resources for others. The sharing of resources among organizations can significantly enhance the practitioners’ capabilities, as partners can work in tandem on sustainability initiatives and innovation projects to achieve circular economy outcomes. The stakeholders’ pooling of surplus resources can lower the manufacturing costs for collaborating partners, as they allow them to access tools and materials at lower market prices.
The case of Kalundborg, Denmark, typifies such open innovation approaches (CEStakeholderEU n.d.; Valenzuela-Venegas et al. 2016). A power plant (located at Asnæs), a Novo Nordisk (a pharmaceutical company), and an oil refinery (belonging to Equinor, formerly known as Statoil), among other organizations, are working together in industrial symbiosis. In sum, these entities have created a network that optimizes materials from waste or by-products and are turning them into valuable resources. Their aim is to lower their costs while minimizing their environmental impact.
Kalundborg started as an informal exchange of waste materials between industries that are situated in close proximity to one another. For example, the excess heat from the power plant is used by Novo Nordisk for production processes, and to heat local homes. In addition, surplus water from the oil refinery is used by a local fish farm. Over the years, this collaboration has grown into a large-scale, highly efficient system, where waste from one process becomes a resource for another. Such symbiosis has significantly reduced waste, emissions, and water consumption, thereby contributing to environmental and economic sustainability.
Similarly, the municipality of Amsterdam is collaborating with a nonprofit organization, entitled, “Circle Economy.” Together, they have developed a strategic plan whose objectives are to turn Amsterdam into a fully circular city by 2050 (Calisto Friant et al. 2021; CEStakeholderEU 2016; Government.nl 2016). This initiative involves the transformation of various sectors, such as construction, energy, and waste management, among others, to adapt the city to operate closed-loop systems. Collaborative projects comprise the reutilization of materials from demolished buildings to reduce waste generated from the construction industry, the promotion of business models like “product as a service” that encourage the leasing of assets rather than owning them, the development of shared mobility solutions, and the reduction of food waste, among others (Camilleri 2021; Camilleri 2025). These circular economy practices can contribute to reducing resource utilization, consumption, and depletion of materials.
Resource Recovery, Reverse Logistics, and Product-Life Extension Strategies
Practitioners can collaborate with external partners to extend the life of certain products and/or of their components. They can help each other to recover materials from used and unwanted items, including from waste, in order to reuse, refurbish, recycle, and remanufacture resources to promote sustainable supply chains (Hadi 2024). The resource recovery procedures focus on reclaiming discarded products and their component materials to reuse them as inputs for new production processes (Brown et al. 2020). Similarly, reverse logistics approaches are intended to support the collection and transportation of waste items, like plastics, metal, and electronics, among others (Pichlak and Szromek 2022). For example, returned electronics can be refurbished, remanufactured for further use, and resold. Such operational processes facilitate the flow of products in the opposite direction of traditional supply chains, as they involve returning, repairing, restoring, and recycling materials for a specific manufacturer, or for designated facilities.
The utilized materials that could have finished in a landfill can be repurposed as plausible resources in industrial production (Lisi et al. 2024). Likewise, the products collected through reverse logistics can also be refurbished or remanufactured. This form of resource recovery extends the life of products and reduces the need for new raw materials (Phonthanukitithaworn et al. 2024). There are instances where materials like organic waste, used oils, or even heat could be captured and utilized in waste-to-energy processes, and for resource extraction purposes, instead of being disposed of, in the natural environment (Ahmad et al. 2024; Liu et al. 2023). Therefore, external stakeholders could help sustainability champions in the recovery of resources, or to increase product longevity, and the lifecycles of extant products and/or of their component materials, while reducing material consumption (Panza et al. 2022; Sgambaro et al. 2024). As a result, the responsible manufacturers would be in a position to develop sustainable products that are durable, repairable, recyclable, and/or biodegradable.
For example, retail brands, including H&M, among others have teamed up with Ellen MacArthur Foundation as well as with philanthropists, nongovernmental organizations (NGOs), and disruptive innovators, to design a “new textiles economy” known as Circular Fibres Initiative (Ellen MacArthur Foundation 2021a; UNEP 2023). One of its objectives is to develop materials including sustainable fibers in order to improve their end-of-life processing. As a result, clothing and apparel materials could last longer, be worn multiple times, and may be easily rented, resold, or recycled. This collaboration set the foundation for H&M’s efforts to collect and recycle used clothing through their in-store garment collection programs. Similarly, Nike has launched a Circular Innovation Challenge (Di Summa 2023). Like H&M, it invited innovators from around the world to propose ideas for new sustainability materials, design processes, and end-of-life solutions for shoes, to transform the future of footwear. Evidently, Nike’s goal was to reduce waste by creating closed-loop products that are recycled or reused at the end of their lifecycle. One of the major outcomes of their challenge was the development of shoes made from recycled materials, including from factory waste and recycled plastics.
Like Nike, Adidas partnered with Parley for the Oceans, an environmental organization, as well as with material innovators and recycling experts, to address a growing consumer demand for eco-friendly and sustainable footwear, without compromising on performance or quality (Murfree and Police 2022). This collaboration is aimed at developing shoes made from recycled ocean plastics, thereby contributing to a circular product lifecycle. As a result, the company’s Parley line of shoes, which was/is made from ocean plastics, has quickly become a global success, with millions of pairs sold since its launch. Other apparel brands, including Patagonia, REI, and Eileen Fisher, have joined forces with Yerdle, a technology company that provides logistics capabilities to buy back and resell their used items (Agrawal et al. 2019; Forbes 2019). By taking advantage of resale, brands take control of the growing secondary retail market. Such sustainable recovery practices provide them with an opportunity to extend the life of their existing products. Hence, they are in a position to reduce the generation of unwanted materials that end up in landfills. At the same time, they promote responsible consumption behaviors among consumers, and increase their profits, by selling refurbished items.
Alternatively, for-profit businesses may collaborate with other organizations, including with competitors, to reduce waste related to single-use packaging, that could inevitably end up in landfills, and/or in our oceans. TerraCycle, a United States–based company specializing in recycling hard-to-recycle materials, is a case in point, of such organizations, as its “Loop” platform aims to reduce single-use packaging, by offering consumers reusable, refillable containers for everyday products (Conick 2019; WEF 2023). Launched in 2019, Loop represents a major step toward implementing circular economy principles. It is intended to eliminate waste from disposable packaging through a “return and reuse” system. For the record, Terracycle entered into a partnership with multinational brands like Nestlé, Unilever, and Procter & Gamble, among other retailers Consumers can purchase these brands’ products through Loop’s platform, and when finished, they can return their empty packages for cleaning and reuse. The partnerships among these big brands has dramatically reduced the need for single-use plastic packaging. As a result, a number of companies have been able to extend the lifecycle of their packaging materials, while offering consumers a more sustainable alternative to traditional packaging. The Loop model has expanded to major retailers like Carrefour in Europe and Walgreens in the United States, among others, demonstrating that open innovation efforts across different sectors can scale circular practices globally (WEF 2025).
For instance, there is scope for businesses to collaborate with research institutions as well as with NGOs, to develop open innovation solutions that are intended to reduce waste and pollution that are damaging the natural environment and the biosphere (Pichlak and Szromek 2022). For instance, Interface (a flooring company) and the Zoological Society of London have launched the Net-Works Program (Luqmani et al. 2017; ZSL 2025). Essentially, this program involves the utilization of discarded fishing nets and their recycling into nylon yarn, to develop sustainable carpets. Net-Works is designed to tackle the growing environmental problem of discarded fishing nets in some of the globe’s poorest coastal communities, including those in the Philippines and Cameroon, among others. This program is aimed at reducing pollution in the oceans, as plastic materials can be ingested by marine animals and/or destroy their habitat. It raises awareness on the use of dangerous resources that are polluting the world’s natural environment. Moreover, it offers economic opportunities for the governments of developing countries, as they enable them to provide new sources of income for local communities. Through such sustainable initiatives, Interface has integrated a circular economy approach into its supply chain. It created a model that combines environmental conservation with social impact.
In a similar vein, Unilever, one of the world’s largest consumer goods companies, is collaborating with external innovators, research institutions and startups to address the challenge of plastic waste. In short, this multinational business indicated that it is seeking external ideas to reduce plastic waste, to use better plastic that is designed to be recycled, and/or to avoid using plastic by switching to alternative materials (Arijeniwa et al. 2024; Phelan et al. 2022). Unilever’s engagement with external partners has helped the organization to utilize responsible material designs, sustainable packaging, and recycling technologies that align with circular economy principles. For example, one of the key success factors of Unilever’s open innovation initiative was the development of a fully recyclable plastic detergent bottle that is made from 100% recycled materials. Additionally, this multinational organization continuously raises awareness about its reuse and refill stations for personal care products, in various supermarkets, in different contexts around the globe, thereby reducing the need for single-use packaging. The diverse ideas sourced through external partners are significantly contributing to minimizing the use of virgin plastics by its distributors in the value chains, as well as by their consumers.
Likewise, Proctor & Gamble (P&G) collaborates with external scientists, startups, research institutions, and industry partners in its Connect + Develop program that is intended to develop sustainable products and solutions (Huston and Sakkab 2006). This laudable program seeks external ideas related to sustainable packaging and product designs that are congruent with the company’s circular economy goals. Since its inception, P&G has developed new packaging materials that are easier to recycle, such as its clear, recyclable plastic for shampoo bottles. The company has also introduced concentrated product formulations that reduce packaging waste and shipping emissions. P&G’s open innovation model allowed the company to access diverse ideas and to rapidly implement responsible and sustainable solutions that align with its circular economy vision.
Another good example of circular economy practices is clearly illustrated when organizations leverage open innovation approaches to adopt waste-to-resource technologies to accelerate their transition to a zero-waste economy. A number of manufacturing firms including automotive businesses are already recovering materials and reutilizing resources from used vehicles at their end-of-life. Renault, one of Europe’s largest car makers, has teamed up with Veolia, a global environmental services company and Solvay, a global chemical and advanced materials company, to develop closed-loop recycled resources for automotive parts (Ellen MacArthur Foundation 2021b; Muller et al. 2021). These companies collaborate to utilize end-of-life vehicles to recover metals, plastics and other materials from them, as they are no longer in use. This allows Renault to operate its business sustainably, as the French car maker incorporates recycled materials in its new automobiles. The automotive company’s manufacturing plant in Flins, France, became a leading facility in Europe for vehicle disassembly and material recovery, thereby contributing to the circular economy agenda.
Product-Service Systems/Product-as-a-Service
Other manufacturing practitioners operating in different industries are adopting product-service systems that are also known as product-as-a-service business models. Such circular economy approaches involve companies offering products in combination with services (Sgambaro et al. 2024). The businesses offering product-service systems emphasize about the value derived from accessing and utilizing their maintained products rather than owning them. This economic model clearly specifies that customers do not have to purchase the products they use. Hence, consumers would benefit from utilizing the products and from its performance. Frequently, the practitioners operating business models that are very similar to leasing systems would provide additional services including maintenance, upgrades, and training, among others, along with their products, to add value to customers. As the service providers would usually retain the ownership of their products, it is in their interest to design them as efficient as possible, as they are meant to serve their purpose for a long time, without the need for regular maintenance (Chen 2018). Preferably, they should be designed in a very sustainable manner. Their components ought to be easily recyclable, and preferably modular and lightweight, to increase their likelihood of offering extended product lifespans.
A case in point is Signify (that was formerly known as Philips Lighting). Currently, the Dutch multinational conglomerate is collaborating with various municipalities and businesses (Bocken 2021; Camilleri 2019). The company is adopting a product-service system strategy, as it provides lighting systems as a service to its clients including to municipalities and to businesses, rather than merely selling light bulbs. This enables Signify to retain ownership of its equipment, to maintain its infrastructure as well as to upgrade and recycle its products at their end-of-life. In plain words, its customers will be only expected to pay for the light they use.
Arguably, this business model is clearly promoting the circular economy. It encourages the manufacturers and/or service providers to use efficient materials, as well as to increase the recycling of resources and materials. Hence, they will be in a better position to reduce their waste.
Sharing Economies and Leasing Systems
There are other sustainable business models that are related to product-service systems (Sergianni et al. 2024). In this case, their payment structure is typically based on subscription models, leases, and/or may involve pay-per-use arrangements. Customers including individuals and organizations, such as institutions, businesses, and NGOs, will be expected to pay for the duration of the service(s) they receive, or to pay the amount of the products they consume. Like the product-service systems (that were mentioned in the previous section), such circular economy models are shifting the focus from ownership to access (Eisenreich et al. 2021).
Such sustainable propositions can extend product lifecycles, reduce the generation of waste, and encourage resource-efficient practices. The proprietors who lease their assets are responsible for their ongoing maintenance and repairs. Hence, it is in their interest to design and develop high-quality, durable items and components that are easy to replace, refurbish, recycle, and repair. If they do so, they would require fewer raw materials, minimize their reliance on new resources, and also decrease their waste output.
The partnership between FROG Bikes (a manufacturer of children’s bikes) and Bike Club (a subscription service for bikes) represents a good example of open innovation practices, as the two businesses joined forces to lease bikes for families, and to exchange bikes as children outgrow them (Eurofound 2018). Essentially, Frog Bikes maintains, refurbishes, and reuses its bikes with new customers, once existing consumers need to upgrade to bigger ones. They strive in their endeavors to maximize the use of their resources. In reality, such a sharing economy initiative has extended the life of the bikes and has significantly reduced the likelihood that they end up in landfills when kids outgrow them. Indeed, the Bike Club’s leasing model is promoting a circular approach by prioritizing maintenance, reuse, and resource efficiency, over ownership and disposal.
Similarly, Floow2, a Dutch business-to-business sharing platform, collaborates with hospitals, construction companies, and other firms to share underutilized equipment, vehicles, and office spaces (Ellen MacArthur Foundation 2021c). This sharing economy company invites businesses from various industry sectors, including healthcare and construction, among others, to list their idle assets (that can be rented). Floow2 facilitates the sharing economy of high-cost resources such as medical equipment and/or construction tools. Its platform enables its customers (including hospitality, clinics, healthcare centers, and construction companies, among others) to optimize their operations, by utilizing leased technologies and systems, without the need to purchase them. This sharing economy approach reduces unnecessary investments in new equipment, minimizes waste, and improves resource efficiencies across multiple sectors.
Discussion
This research raises awareness of practitioners’ crowdsourcing initiatives and collaborative approaches, such as sharing ideas and resources with external partners, expert consultants, marketplace stakeholders (like suppliers and customers), university institutions, research centers, and even competitors, as the latter can help them develop innovation labs and to foster industrial symbiosis (Calabrese et al. 2024; Sundar et al. 2023; Triguero et al. 2022). It reported that open innovation networks would enable them to work in tandem with other entities to extend the life of products and their components. It also indicated how and where circular open innovations would facilitate the sharing of unwanted materials and resources that can be reused, repaired, restored, refurbished, or recycled through resource recovery systems and reverse logistics approaches. In addition, it postulates that circular economy practitioners could differentiate their business models by offering product-service systems, sharing economies, and/or leasing models to increase resource efficiencies and to minimize waste.
Arguably, the cocreation of open innovations can contribute to improve the financial performance of practitioners as well as of their partners who are supporting them in fostering closed-loop systems and sharing economy practices. They enable businesses and their stakeholders to minimize externalities like waste and pollution that can ultimately impact the long-term viability of our planet. Figure 1 presents a conceptual framework that clarifies how open innovation cocreation approaches can be utilized to advance circular, closed-loop models while adding value to the businesses’ financial performance.
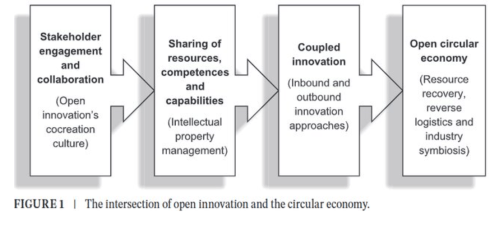
The collaborative efforts between organizations, individuals, and various stakeholders can lead to sustainable innovations, including to the advancement of circular economy models (Jesus and Jugend 2023; Tumuyu et al. 2024). Such practices are not without their own inherent challenges and pitfalls. For example, resource sharing, the recovery of waste and by-products from other organizations, and industrial symbiosis involve close partnership agreements among firms and their collaborators, as they strive in their endeavors to optimize resource use and to minimize waste (Battistella and Pessot 2024; Eisenreich et al. 2021). While the open innovation strategies that are mentioned in this article can lead to significant efficiency gains and to waste reductions, practitioners may encounter several difficulties and hurdles, to implement the required changes (Phonthanukitithaworn et al. 2024). Different entities will have their own organizational culture, strategic goals, and modus operandi that may result in coordination challenges among stakeholders.
Organizations may become overly reliant on sharing resources or on their symbiotic relationships, leading to vulnerabilities related to stakeholder dependencies (Battistella and Pessot 2024). For instance, if one partner experiences disruptions, such as operational issues or financial difficulties, it can adversely affect the feasibility of the entire network. Notwithstanding, organizations are usually expected to share information and resources when they are involved in corporate innovation hubs and clusters. Their openness can lead to concerns about knowledge leakages and intellectual property theft, which may deter companies from fully engaging in resource-sharing initiatives, as they pursue outbound innovation approaches.
Other challenges may arise from resource recovery, reverse logistics, and product-life extension strategies (Johnstone 2024). The implementation of reverse logistics systems can be costly, especially for small and micro enterprises. The costs associated with the collection, sorting, and processing of returned products and components may outweigh the benefits, particularly if the market for recovered materials is not well established (Panza et al. 2022; Sgambaro et al. 2024). Moreover, the effectiveness of resource recovery methodologies and of product-life extension strategies would be highly dependent on the stakeholders’ willingness to return products or to participate in recycling programs. Circular economy practitioners may have to invest in promotional campaigns to educate their stakeholders about sustainable behaviors. There may be instances where existing recovery and recycling technologies are not sufficiently advanced or widely available, in certain contexts, thereby posing significant barriers to the effective implementation of open circular innovations. Notwithstanding, there may be responsible practitioners and sustainability champions that may struggle to find reliable partners with appropriate technological solutions that could help them close the loop of their circular economy.
In some scenarios, emerging circular economy enthusiasts may be eager to shift from traditional product sales models to innovative product-service systems. Yet, such budding practitioners can face operational challenges in their transitions to such circular business models. They may have to change certain business processes, reformulate supply chains, and also redefine their customer relationships, to foster compliance with their modus operandi. These dynamic aspects can be time-consuming, costly, and resource intensive (Eisenreich et al. 2021). For instance, the customers who are accustomed to owning tangible assets may resist shifting to a product-service system model. Their reluctance to accept the service providers’ revised terms and conditions can hinder the adoption of circular economy practices. The former may struggle to convince their consumers to change their status quo, by accessing products as a service, rather than owning them (Sgambaro et al. 2024). In addition, the practitioners adopting products-as-a-service systems may find it difficult to quantify their performance outcomes related to resource savings and customer satisfaction levels and to evaluate the success of their product-service models, accurately, due to a lack of established metrics.
In a similar vein, the customers of sharing economies and leasing systems ought to trust the quality standards and safety features of the products and services they use (Sergianni et al. 2024). Any negative incidents reported through previous consumers’ testimonials and reviews can undermine the prospective customers’ confidence in the service provider or in the manufacturer who produced the product in the first place. Notwithstanding, several sharing economy models rely on community participation and localized networks, which can pose possible challenges for scalability. As businesses seek to expand their operations, it may prove hard for them to consistently maintain the same level of trust and quality in their service delivery. Moreover, many commentators argue that the rapid growth of sharing economies often outpaces existing regulatory frameworks. The lack of regulations, in certain jurisdictions, in this regard, can create uncertainties and gray areas for businesses as well as for their consumers.
Read further: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/bse.4216 (the full references are available here).
This research is also available via ResearchGate, Academia.edu, Social Science Research Network and through University of Malta’s Open Access Repository.





You must be logged in to post a comment.