This is an excerpt from one of our latest contributions published through The Service Industries Journal. It features snippets from the ‘Introduction’, ‘Theoretical Implications’, ‘Practical Implications’ as well as from the ‘Limitations and Future Research Avenues’ sections.
Suggested Citation: Camilleri, M.A., Zhong, L., Rosenbaum, M.S. & Wirtz, J. (2024). Ethical considerations of service organizations in the information age, The Service Industries Journal, Forthcoming. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/02642069.2024.2353613
Introduction
Ethics is a broad field of study that refers to intellectual and moral philosophical inquiry concerned with value theory. It is clearly evidenced when individuals rely on their personal values, principles and norms to resolve questions about appropriate courses of action, as they attempt to distinguish between right and wrong, good and evil, virtue and vice, justice and crime, et cetera (Budolfson, 2019; Coeckelbergh, 2021; Ramboarisata & Gendron, 2019). Several researchers contend that ethics involves a set of concepts and principles that are meant to guide community members in specific social and environmental behaviors (De Bakker et al., 2019; Hermann, 2022). Very often, commentators argue that a persons’ ethical dispositions are influenced by their upbringing, social conventions, cultural backgrounds, religious beliefs, as well as by regulations (Vallaster et al., 2019).
Individuals, groups, institutions, non-government entities as well as businesses are bound to comply with the rule of law in their society (Groß & Vriens, 2019). As a matter of fact, the businesses’ organizational cultures and modus operandi are influenced by commercial legislation, regulations and taxation systems (Bridges, 2018). For-profit entities are required to adhere to the companies’ acts of the respective jurisdictions where they are running their commercial activities. They are also expected to follow informal codes of conduct and to observe certain ethical practices that are prevalent in the societies where they are based. This line of reasoning is synonymous with mainstream “business ethics” literature, that refer to a contemporary set of values and standards that are intended to govern the individuals’ actions and behaviors in how they manage and lead organizations (DeTienne et al., 2021).
Employers ought to ensure that they are managing their organization in a fair, transparent and responsible manner, by treating their employees with dignity and respect (Saks, 2022). They have to provide decent working environments and appropriate conditions of employment by offering equitable extrinsic rewards to their workers, that are commensurate with their knowledge, skills and competences (Gaur & Gupta, 2021). Moreover, it is in the employers’ interests to nurture their members of staff’s intrinsic motivations if they want them to align with their organizational values and corporate objectives (Camilleri et al., 2023). Notwithstanding, all businesses, including those operating in service industries have ethical as well as environmental, social and governance (ESG) responsibilities to bear towards other stakeholders in society (Aksoy et al., 2022).
This article raises awareness on a wide array of ethical considerations affecting service organizations in today’s information age. Specifically, its research objectives are threefold: (i) It presents the findings from a rigorous and trustworthy systematic review exercise, focused on “ethics” in “service(s)” and/or “ethical services”. This research involves a thorough scrutinization of the most-cited articles published in the last five (5) years; (ii) It utilizes a thematic analysis to determine which paradigms are being associated with service ethics. The rationale is to identify some of the most contemporary topics related to ethical leadership in service organizations. (iii) At the same time, it puts forward theoretical and practical implications that clarify how, why, where, when and to what extent service providers are operating in a legitimate and ethical manner.
A thorough review of the literature reveals that, for the time being, there are just a few colleagues who have devoted their attention to relevant theoretical underpinnings linked to the service ethics literature (Liu et al., 2023; Wirtz et al., 2023). For the time being, there is still limited research that has outlined popular research themes from the most cited articles published in the past five (5) years. It clearly differentiates itself from previous studies as this contribution’s rigorous and transparent systematic review approach clearly recognizes, appraises and describes the methodology that was used to capture and analyze data focused on the provision or lack thereof of ethical services. In addition, unlike other descriptive literature reviews, this paper synthesizes the findings from the latest contributions on this topic and provides a discursive argumentation on their implications. Hence, this article addresses a number of knowledge gaps in academic literature. In conclusion, it identifies the limitations of this review exercise, and outlines future research avenues to academia.
Theoretical implications
This contribution raises awareness of the underexplored notion of service ethics. A number of commentators are making reference to various theories and concepts to clarify how they can guide service organizations in their ethical leadership. In many cases, a number of theories indicate that decision makers ought to be just and fair with individuals or entities in their actions. Appendix A features a list of ethical theories and provides a short definition for them. For instance, the justice theory suggests that all individuals including service employees should have the same fundamental rights based on the values of equality, non-discrimination, inclusion, human dignity, freedom and democracy. Human rights as well as employee rights and values ought to be protected and reinforced by the respective jurisdictions’ rule of law, for the benefit of all subjects (Grégoire et al., 2019).
Business ethics literature indicates that just societies are characterized by fair, trustworthy, accountable and transparent institutions (and organizations). For instance, the fairness theory raises awareness on certain ethical norms and standards that can help policy makers as well as other organizations including businesses, to ensure that they are continuously providing equal opportunities to everyone. It posits that all individuals ought to be treated with dignity in a respectful and equitable manner (Wei et al., 2019).
This is in stark contrast with the favoritism theory that suggests that certain individuals including employees, can receive preferential treatment, to the detriment of others (Bramoullé & Goyal, 2016). This argumentation is synonymous with the nepotism theory. Like favoritism, nepotism is a phenomenon that is manifested when institutional and organizational leaders help and support specific persons because they are connected with them in a way or another (e.g. through familial ties, friendships, financial, or social factors). Arguably, such favoritisms clearly evidence their conflict(s) of interest, compromise or cloud their judgements, decisions and actions in workplace environments and/or in other social contexts. Many business ethics researchers contend that decision makers ought to be guided by the principle of beneficence (Brear & Gordon, 2021), as they should possess the competences and abilities to recognize between what is morally right and ethically wrong.
This research confirms that frequently, organizational leaders have to deal with difficult and challenging situations, where they are expected to make hard decisions (Islam et al., 2021a; Islam et al., 2021b; Latan et al., 2019; Naseer et al., 2020; Schwepker & Dimitriou, 2021). In such cases, the most reasonable ethical approach would be to follow courses of action that will result in the least possible harm to everyone (Heine et al., 2023). The service organizations’ members of staff are all expected to be collaborative, productive and efficient in their workplace environment. This line of reasoning is related to the attributional theory (Bourdeau et al., 2019) and/or to the consequentialism theory (Budolfson, 2019). Very often, the proponents of these two theories contend that while honest, righteous and virtuous behaviors may yield positive outcomes for colleagues, subordinates and other stakeholders, wrong behaviors can result in negative repercussions to them (Deci & Ryan, 1987; Francis & Keegan, 2020; Lee et al., 2020; Paramita et al., 2021)
Other researchers who contributed to the ethics literature related to the utilitarianism theory, suggest that people tend to make better decisions, when they focus on the consequences of their actions. Hence, they will be in a better position to identify laudable behaviors and codes of conduct that add value to their organization (Coeckelbergh, 2021; Michaelson & Tosti-Kharas, 2019; Ramboarisata & Gendron, 2019). Very often, they argue that there are still unresolved issues in social sciences including the unpredictability of events and incidents from happening (Du & Xie, 2021), and/or the difficulty in measuring the consequences when/if they occur. For example, this review indicated that various authors discussed about the challenges, risks and possible dangers of adopting various technologies including AI, big data, et cetera (Breidbach & Maglio, 2020; Chang et al., 2020; Flavián & Casaló, 2021; Rymarczyk, 2020). In many cases, they hinted that the best ethical choice is to identify which decisions and actions could lead to the greatest good, in terms of positive, righteous and virtuous outcomes (Budolfson, 2019; Gong et al., 2020; Paramita et al., 2021).
Various academic authors who contributed to the formulation of the virtues theory held that there are persons including organizational leaders, whose characters, traits and values drive them to continuously improve and to excel in their duties and responsibilities (Coeckelbergh, 2021; Fatma et al., 2020; Lee et al., 2020). They frequently noted that the persons’ affective feelings as well as their intellectual dispositions enable them to develop a positive mindset, to make the best decisions and to engage in the right behaviors (Gong et al., 2020; Huang & Liu, 2021; Yan et al., 2023). This is congruent with the theory of positivity too, as it explains how the individuals’ optimistic feelings may result in their happiness and wellbeing. Some commentators imply that such positive emotions can influence the individuals’ state of minds and can foster their resilience to engage in productive behaviors (Paramita et al., 2021).
This argumentation is in stark contrast with the emotional labor theory that is manifested when disciplined employees suppress their emotions by engaging in posturing behaviors in order to conform to the organizational culture (Mastracci, 2022). This phenomenon was evidenced in Naseer et al.’s (2020) contribution. In this case, the authors indicated how the employees’ overidentification with unethical organizations can have a negative impact on their engagement, thereby resulting in counterproductive work practices. In addition, Islam et al. (2021b) also suggested that abusive supervision led employees to undesirable outcomes like knowledge hiding behaviors and to low morale in workplace environments.
Several commentators who are focused on psychological issues argue that the individuals’ intrinsic motivations are closely related to their self-determination (Deci & Ryan, 1987). Very often, they contend that individuals should have the autonomy and freedom to make life choices, in order to improve their well-being in the future. The findings from this research reported that organizational leaders who delegated responsibilities to their members of staff, have instilled trust and commitment in their employees, and also improved their intrinsic motivations (Francis & Keegan, 2020; Lee et al., 2020; Schwepker & Dimitriou, 2021).
Hence, organizational leaders of service businesses ought to be aware that there is scope for them to empower their human resources, to help them make responsible choices and decisions relating to their work activities, in a discrete manner (Bourdeau et al., 2019; Islam et al., 2021a; Tanova & Bayighomog, 2022). The employees’ higher levels of autonomy and independence can influence their morale (Paramita et al., 2021; Ramboarisata & Gendron, 2019) and reduce stress levels (Schwepker & Dimitriou, 2021). Various researchers confirmed that employees would be more productive if they were empowered with duties and responsibilities (e.g. Nauman et al., 2023).
This argumentation is congruent with the conservation of resources theory, as business leaders are expected to look after their human resources’ cognitive and emotional wellbeing, if they want to foster their organizational commitment to achieve their corporate objectives. Indeed, their ethical leadership can lead to win-win outcomes, particularly if their employees replicate responsible and altruistic behaviors with one another, and if they strive in their endeavors to develop a caring environment in their organization (Parsons et al., 2021; Saks, 2022). This reasoning is closely related to the social cognition theory that presumes that individuals acquire emotional knowledge and skill sets such as intuition or empathy, among others, through social interactions, including when they are at work (Čaić et al., 2019; Campbell et al., 2020; Rauhaus et al., 2020).
Practical implications
The findings from this research confirm that various service organizations are becoming acquainted with ethical leadership and with social issues in management. Evidently, several listed businesses and large undertakings in service industries are increasingly proving their legitimacy and license to operate, by engaging in ethical behaviors that promote responsible human resources management. Very often, they are fostering an organizational climate that encourages ongoing dialogue, communication and collaboration among members of staff; they empower employees with duties and responsibilities to make important decisions; provide them with equitable compensation that is commensurate with qualifications and experience; and implementing work-life balance policies. Generally, these laudable measures are resulting in motivated, committed and productive employees.
On the other hand, unethical behaviors including abusive organizational practices and coercive leadership styles are generating bitterness and feelings of resentment among employees. The lack of ethical leadership can lead to demotivation, low morale, job stress and even to counterproductive behaviors including wrongdoings like knowledge hiding and abusive supervision in workplace environments. This research reported about irresponsible practices of service businesses operating in the sharing economy, as a number of hospitality companies are subcontracting their food delivery services to independent contractors, who are not safeguarding the rights of their employees. Very often, the workers of the gig economy are offered precarious jobs and unfavorable conditions of employment. Generally, they are not paid in a commensurate manner for their jobs, are not eligible for health or retirement benefits, and cannot affiliate themselves with trade unions.
This discursive review shed light on the service businesses’ dealings with employees and with other stakeholders. It also narrated about their relationships with customers as well as on their ethical and digital responsibilities towards them. For example, it indicated that many businesses are gathering and storing data of customers. Frequently, they are using their personal and transactional information to analyze and interpret shopping behaviors. They may do so to build consumer profiles and/or to retarget them with promotional content. The findings of this research imply that it is the responsibility of service businesses to inform new customers that they are capturing and retaining data from them, when and if they do so (even though in many cases, they are aware that many online users can quickly unsubscribe to marketing messages and/or are becoming adept in blocking advertisements from popping-up in their screens). The authors contend that service providers ought to explicitly ask their customers’ consent (through opt-in or opt-out choices) to ensure that the former can avail themselves of their consumers’ data.
Currently, certain jurisdictions are not in a position to protect consumers from entities that could use their personal information for different purposes as they did not enact substantive data protection legislation. The European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), are two examples of data regulations that are intended to safeguard the consumers’ interests in this regard. Online users ought to be educated and guided through regulations, policies and data literacy programs, to protect them from potentially unethical technological applications and practices of big data algorithms and advanced analytics. At the moment, various stakeholders including policy makers and academia, among others, are calling for responsible AI governance and for the formulation of (quasi) regulatory frameworks, in order to maximize the benefits of AI and to minimize its negative impacts to humanity.
This research raises awareness about the importance of disclosing corporate governance procedures, and of regularly reporting CSR/ESG credentials with regulatory stakeholders and with other interested parties. In many cases, the majority of service businesses are genuinely following ethical norms and principles that go beyond their commercial and legal obligations. They should bear in mind that their sustainability accounting, transparent ESG disclosures, as well as their audit and assurance mechanisms, can ultimately reduce information asymmetry among stakeholders, whilst enhancing their reputation and image with interested parties. Their ongoing corporate communications can ameliorate stakeholder relationships and could increase their organizational legitimacy in the long run.
Limitations and future research avenues
The notion of service ethics is gaining traction in academic circles. Indeed, it is considered as a contemporary and timely topic for service researchers specializing in business administration and/or business ethics. In fact, the findings from the bibliographic analysis demonstrate that there were more than eleven thousand (11,000) documents focused on service(s), ethics and ethical service(s), published in the last 5 years. This research adds value to the extant literature as it sheds light on the most cited articles focused on these topics. Yet, it differentiates itself from previous papers, as it identifies the themes of fifty (50) of the most cited papers in this promising area of research, describes the methodology that was employed to capture and analyze the data on this topic, and scrutinizes their content, before synthesizing the findings of this contribution.
This article presents the findings of a rigorous review and evaluation of the latest literature revolving on ethical leadership of service organizations. The authors are well aware that, in the past, other academic colleagues may have referred to synonymous keywords to service ethics or ethical services, including ethical business, business ethos, business ethics, business code of conduct, and even corporate social responsibilities of service businesses, among other paradigms. Therefore, future researchers may also consider using these keywords when they investigate ethical behaviors in services-based sectors. It is hoped that they will delve into the research themes, fields of studies and theoretical bases that were identified in this contribution including on the service organizations’ ethical leadership, as proposed in the following table. This research confirms that it is in the interest of service entities to foster a fair and just working environment, particularly for the benefit of their employees, as well as for other stakeholders including for regulatory institutions, creditors, shareholders and customers, among others.
A future agenda for service ethics research
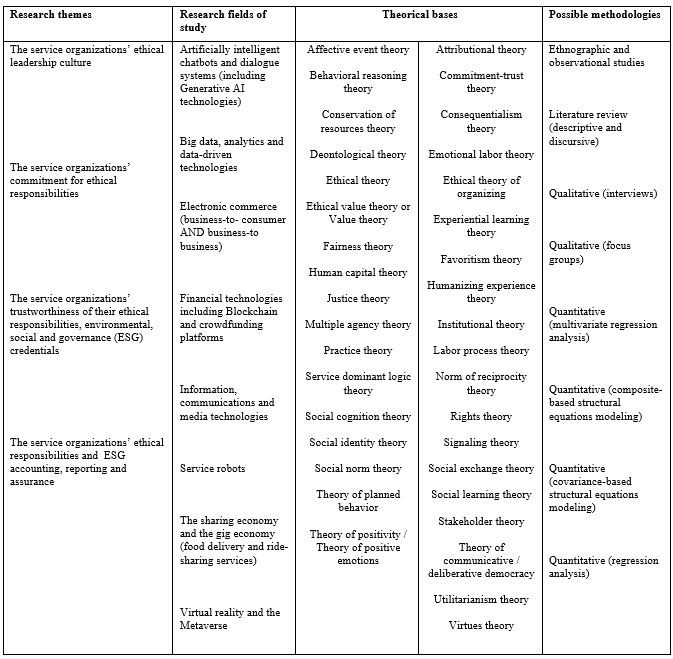
(Developed by the authors)
Indeed, there is scope to investigate further the service organizations’ roles in today’s societies, as they are being urged by policy makers and other interested parties to communicate about their responsible organizational behaviors, in various contexts. Entities operating in service industries including small and medium-sized businesses as well as micro enterprises are increasingly acquainting themselves with sustainability accounting, non-financial reporting and ongoing assurance exercises, as comprehensive CSR/ESG disclosures can enable them to prove their legitimacy and license to operate with stakeholders. Moreover, prospective researchers are invited to continue raising more awareness about ethical leadership among service organizations, particularly when they are adopting disruptive innovations.
The full list of references are available from the open-access article (published through The Service Industries Journal) and via ResearchGate.











You must be logged in to post a comment.